In arbitrary triangle ABC is:
a sin b = c sin a
b sin g = b sin b
c sin a = a sin g
Evidence:
We'll apply demonstration on first three triangles:
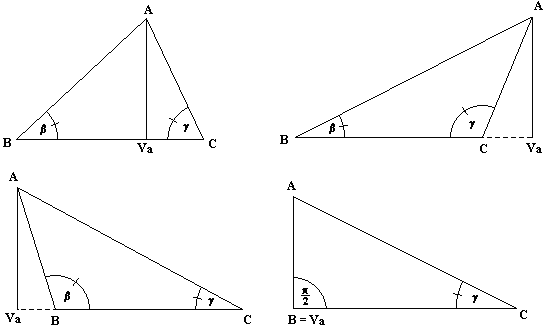
In single situation we have:
Platí teda vždy va = c sin b. Celkom analogickým postupom dostaneme va = b sin g. Z oboch týchto rovností dostávame b * sin g = c * sin b, čo je jedna z rovností v tvrdení vety. Ostatné dve získame analogickým postupom.
